Our data pipelines used to run on Jenkins, a tool we originally chose for CI/CD automation in DevOps. While Jenkins excels at software builds and deployments, it was never designed for dynamic, fault-tolerant, and large-scale data workflows. As our data volume and tenant base grew, limitations started to surface.
Challenges we faced
- Static Workflow Management: Jenkins supports static pipelines, but adding or changing workflows requires manual scripting, slowing down iteration and increasing the risk of errors.
- Lack of Fault Tolerance: Failures often require manual recovery, causing downtime and risking data consistency.
- Scalability Issues: Scaling to large datasets and complex workflows creates performance bottlenecks.
- Limited Monitoring: Native Jenkins lacks real-time monitoring and alerting for data workflows, making issue resolution reactive.
- Centralized Control: Teams depend on Jenkins admins to update workflows, reducing agility and slowing innovation.
Why We Needed a New Approach
We identified the need for a modern orchestration system designed to:
- Dynamically create workflows (DAGs).
- Recover gracefully from failures.
- Scale with data and tenants.
- Provide real-time observability.
- Empower teams to self-serve, without bottlenecking on central admins.
Our Solution Strategy
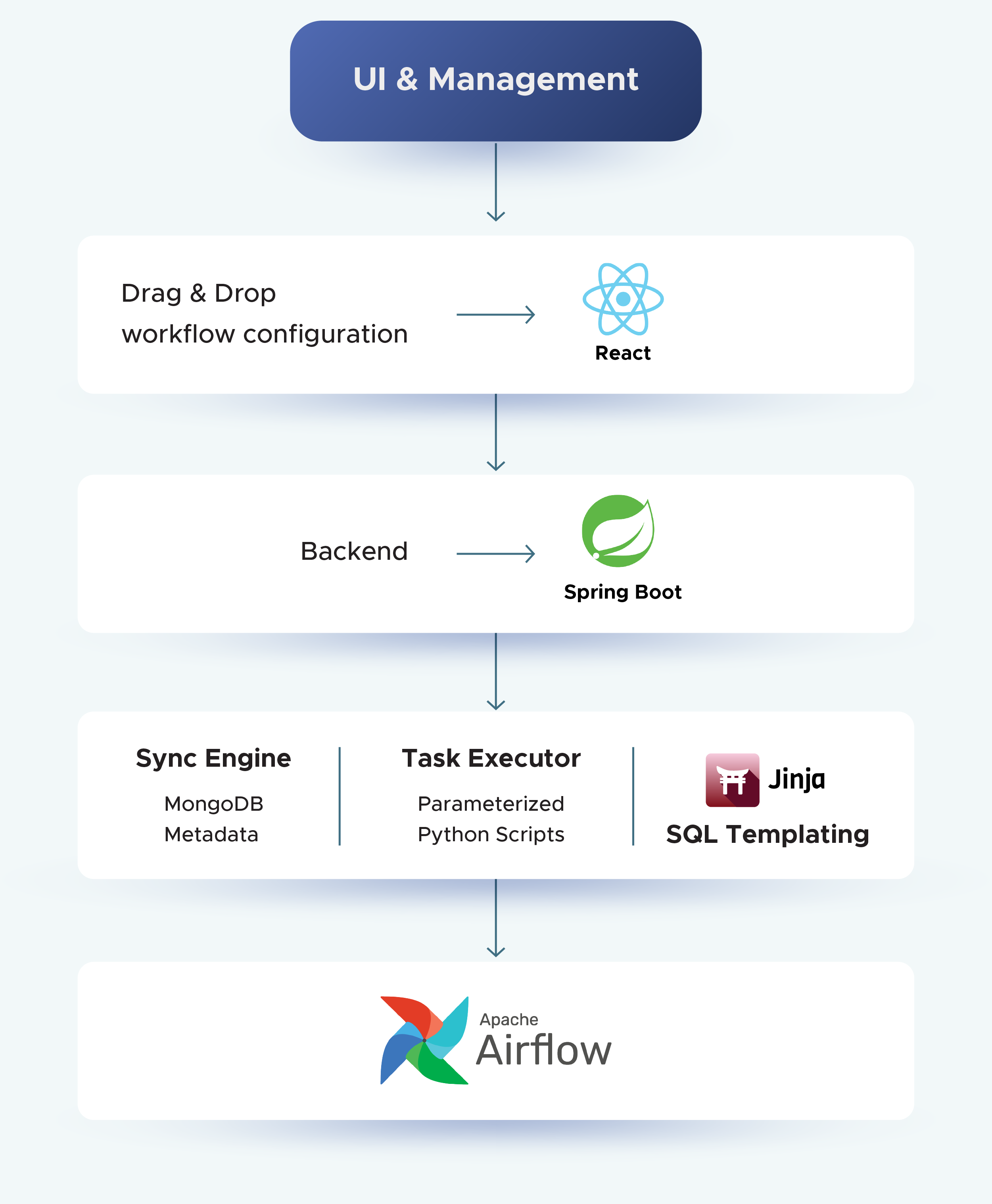
We identified Apache Airflow as the right fit for orchestration and built a custom orchestration framework on top of it, guided by principles of modularity, reuse, and user-friendliness. Instead of fully replacing Jenkins, we positioned both tools where they deliver the most value:
How the New System Works
Our new orchestration platform is designed to balance user-friendliness for pipeline creators with robust orchestration under the hood. Here’s how it works end-to-end:
1. User Interface for Pipelines
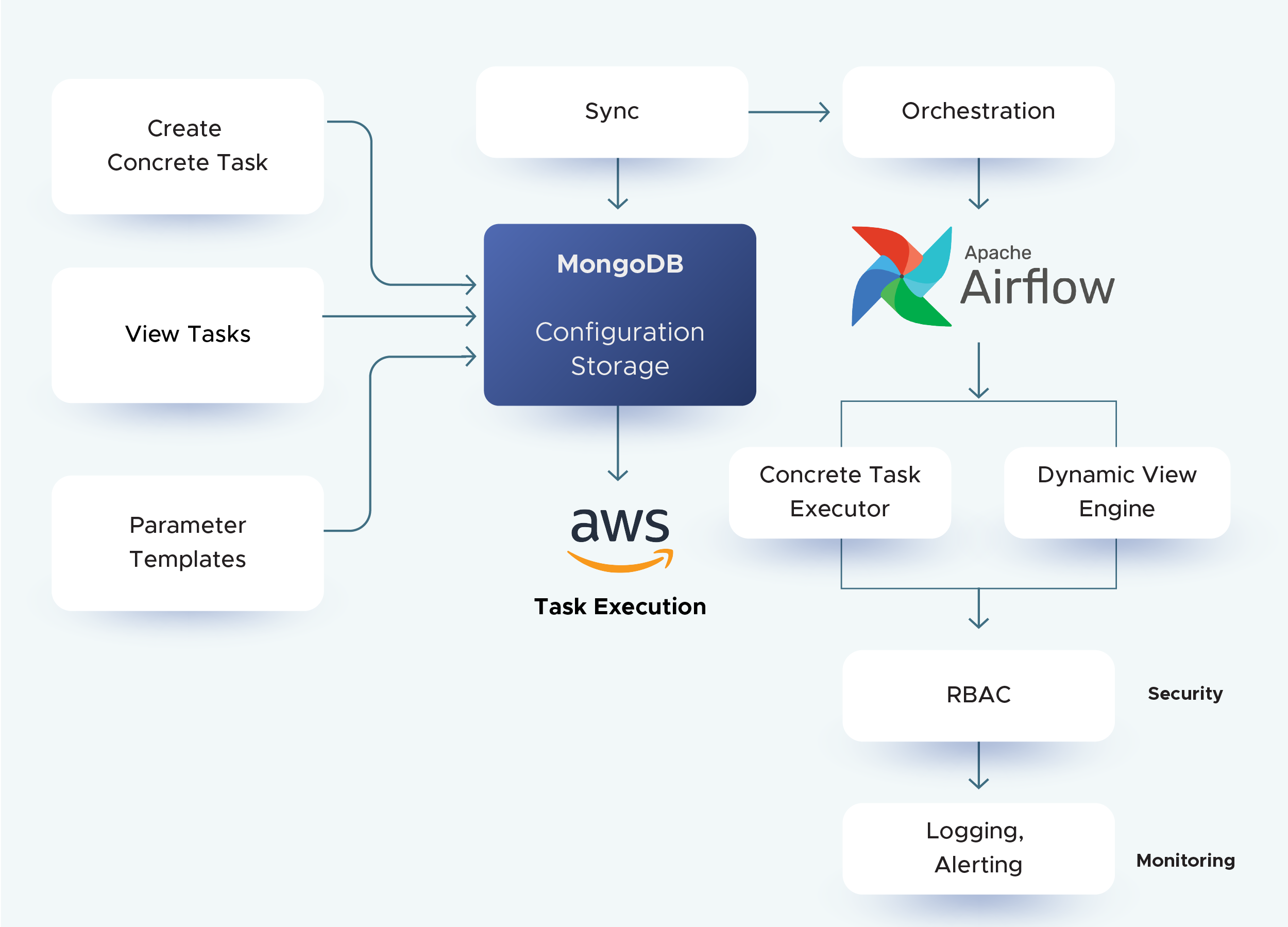
- Users interact with a simple UI to create Concrete Tasks, View Tasks, Parameter Templates, and Pipelines.
- Each component is stored in MongoDB, ensuring persistence and version control.
- Reusable tasks and parameter templates make building pipelines fast and consistent.
- Every pipeline version is tracked, enabling rollbacks to previous configurations when needed.
2. Integration with Apache Airflow
- Once pipelines are defined in MongoDB, configurations are synchronized with Apache Airflow.
- Airflow orchestrates execution: handling dependencies, scheduling, retries, and tracking.
- To support this dynamic execution, we developed three internal systems (distributed as wheel packages) integrated into the Airflow runtime:
a) Sync Engine → pulls pipeline/task definitions from MongoDB into Airflow.
b) Concrete Task Executor → executes Python-based tasks with appropriate parameters.
c) Dynamic View Engine → renders SQL-based tasks at runtime using Jinja templates.
3. Task Execution with AWS Fargate
- For resource-intensive or long-running tasks, Airflow delegates execution to AWS Fargate.
- Tasks run in serverless, isolated containers, ensuring scalability and preventing Airflow workers from being overloaded.
4. Security, Reliability & Maintainability
- Retries & Fault Tolerance: Failed tasks automatically retry, reducing manual intervention.
- RBAC: Role-Based Access Control enforces secure and permissioned access. In AWS, RBAC can be enforced with AWS IAM.
- Observability: Airflow’s monitoring, logging, and alerting give teams real-time visibility into pipeline health and execution.
Impact & Results
- 30% Faster Development – Reusable templates reduced onboarding time and sped up pipeline creation.
- <5% Manual Intervention – Automatic retries improved fault tolerance and reduced recovery overhead.
- Elastic Execution – AWS Fargate enabled scalable, multi-tenant task processing.
- Improved Observability – Real-time monitoring and alerts enhanced reliability.
- Team Autonomy – Self-service pipeline creation reduced central dependencies.
Final Takeaways
Moving from Jenkins-only pipelines to an Airflow-based orchestration framework allowed us to balance scalability, resilience, and usability. The journey reinforced a key principle: the right abstractions and tools enable teams to move faster, with confidence.