Whenever new resources are created in the cloud, one of the recurring tasks of DevOps and Cloud engineers is to ensure they are cost-effective and to implement strategies for reducing unnecessary expenses. A common approach is to schedule resources to automatically start and stop during off-hours and weekends, preventing them from running when not needed and aligning with AWS best practice of paying only for what you use.
Each time new resources are added, these scripts must be updated, and error handling must be implemented to account for resources that may be deleted, ensuring the scheduling process remains uninterrupted for other resources. This approach requires scripting expertise and ongoing maintenance, as any team member wanting to schedule a resource must modify the script. To simplify managing cloud infrastructure, AWS offers straightforward solutions for starting and stopping resources using AWS APIs and custom templates, eliminating the need for complex, manually maintained scripts.
When it comes to automating infrastructure operations, both AWS EventBridge Scheduler and CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler provide robust capabilities, though each brings its own unique approach and feature set.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler vs. CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler
A Deep Dive into Technical Feature Comparison
Here’s a technical breakdown of how CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler and AWS EventBridge Scheduler differ across key scheduling features.
1. Scheduling Features
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Uses a custom template for scheduling, streamlining the process for supported resources. This makes scheduling start/stop actions quick and straightforward, especially for users focused on resource optimization.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Offers two scheduling options:
- One-time (one-off) schedules
- Recurring schedules using cron or rate expressions
This flexibility supports a wide range of automation scenarios, from simple to complex, and enables precise time-based control.
2. Retry Mechanism and Failure Handling
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Has a backend retry mechanism. If throttling occurs, retries are visible in the event dashboard. Once the default retry limit is reached, it waits for the next scheduled interval before attempting again. There is no dead-letter queue (DLQ) integration.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Provides advanced delivery controls:
- Configurable maximum event age
- Retry attempts with delayed retries
- Failed events can be moved to dead-letter queues (DLQs) for further analysis or reprocessing.
3. Resource Identification
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Automatically fetches resources for start/stop operations. Users don’t need to manually input instance IDs or ARNs, simplifying setup for supported resource types.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Requires explicit resource identifiers (such as instance IDs or ARNs) in the API payload for each scheduled action.
4. Supported Operations
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Focused solely on start/stop operations for a select set of AWS resources (e.g., EC2, RDS, ECS).
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Supports a much broader range of operations, including:
- Running ECS tasks
- Invoking Lambda functions
- Triggering Step Functions
- Sending messages to SQS/SNS
- Any API operation can be scheduled, provided the correct resource identifier is supplied.
5. Scheduler Setup
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Start/stop operations are configured through a single template, making setup fast and user-friendly for supported actions.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Requires creation of separate schedules for each action (e.g., one for start, one for stop), which can increase setup complexity for resource lifecycle management.
6. Batching and State Management
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Maintains the state of resources before and after scheduling, ensuring resources return to their original state after scheduled actions. This is particularly helpful for environments where state consistency is critical.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Some AWS APIs support batch operations (e.g., starting/stopping multiple EC2 instances at once). For Auto Scaling Groups, users must specify desired, max, and min capacities, but the scheduler does not maintain resource state. For ECS, separate schedules are needed per service.
7. Grouping
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Does not support grouping of schedules. Each schedule is managed individually.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Supports Scheduler Groups for logical organization (e.g., by environment or application), making it easier to manage large numbers of schedules at scale.
8. Flexible Time Window
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler:
Does not support flexible time windows; actions occur at the scheduled time.
AWS EventBridge Scheduler:
Includes a flexible time window feature, allowing scheduled actions to execute within a defined interval (e.g., between 9:00–9:05 PM). This helps spread out actions, reduces throttling, and improves reliability for large-scale operations.
Let us understand with an example.
Use Case
If we want to start an ASG every weekday at 9 AM using AWS Eventbridge Scheduler:
Step 1: Specify Schedule Details
- Provide a Name for this schedule ( Non-ProdASG_Start)
- Description: Optionally, provide a description like Increase ASG capacity during business hours.
- Select Schedule Group: Each schedule needs to be placed in a schedule group. By default, a schedule is placed in the 'Default' group. You can also create your schedule group. You can only add tags to a schedule group, not a schedule.
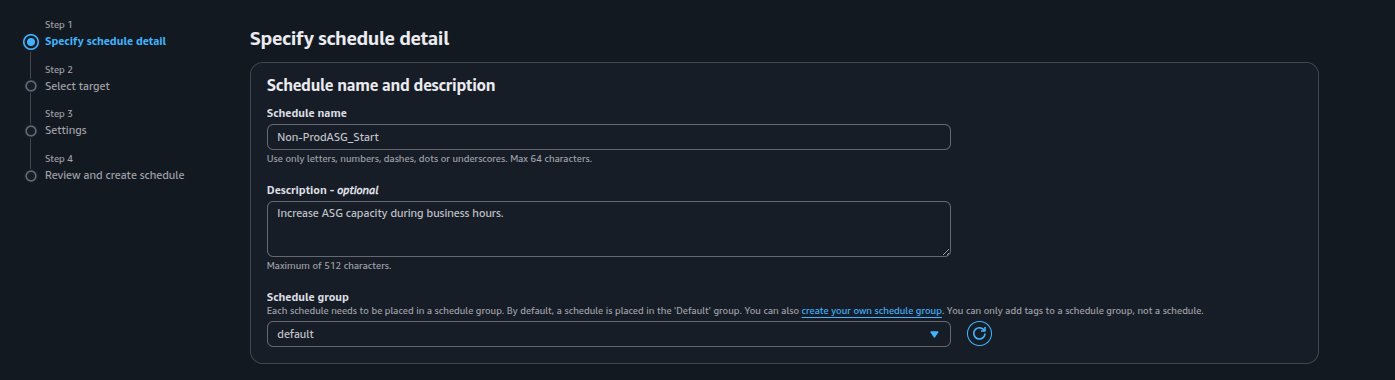
- Choose a schedule pattern
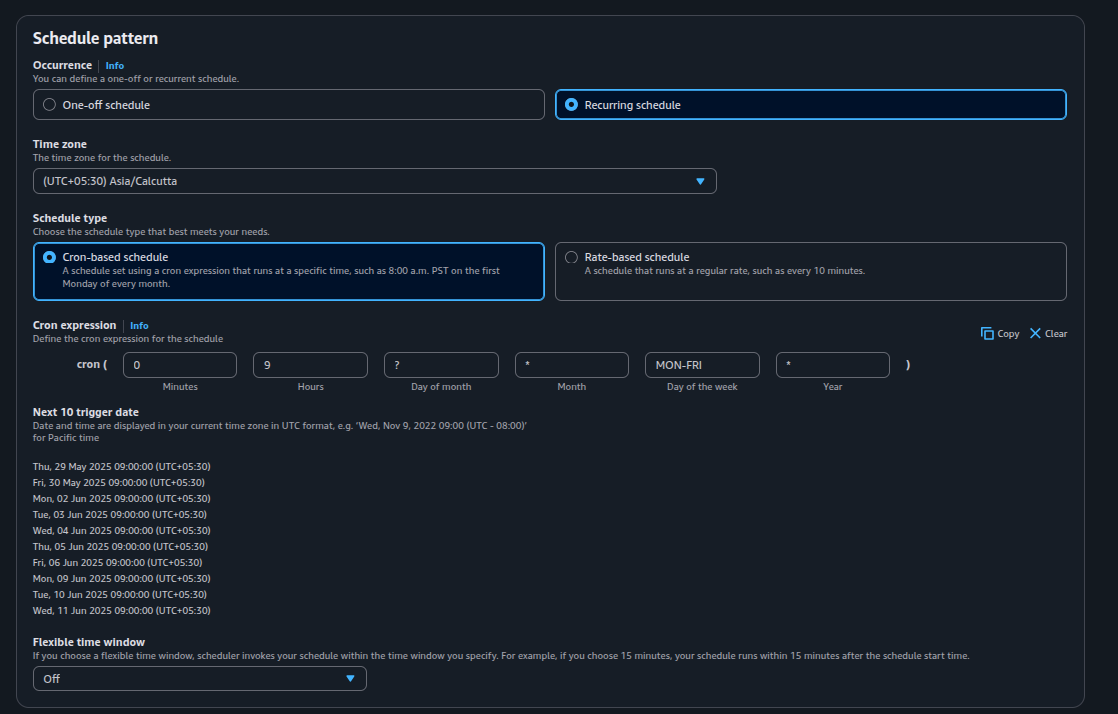
- Schedule type: Select "Recurring".
- Schedule pattern: Choose "Cron expression".
- Cron expression: Enter a cron expression that defines when the scaling action should occur. For example:
- 0 9 ? * MON-FRI * — Triggers at 9:00 AM UTC, Monday through Friday.
- Time zone: Select your desired time zone, such as Asia/Kolkata.
- Set a cron expression, such as cron(0 9 ? * MON-FRI *) for 9 AM on weekdays.
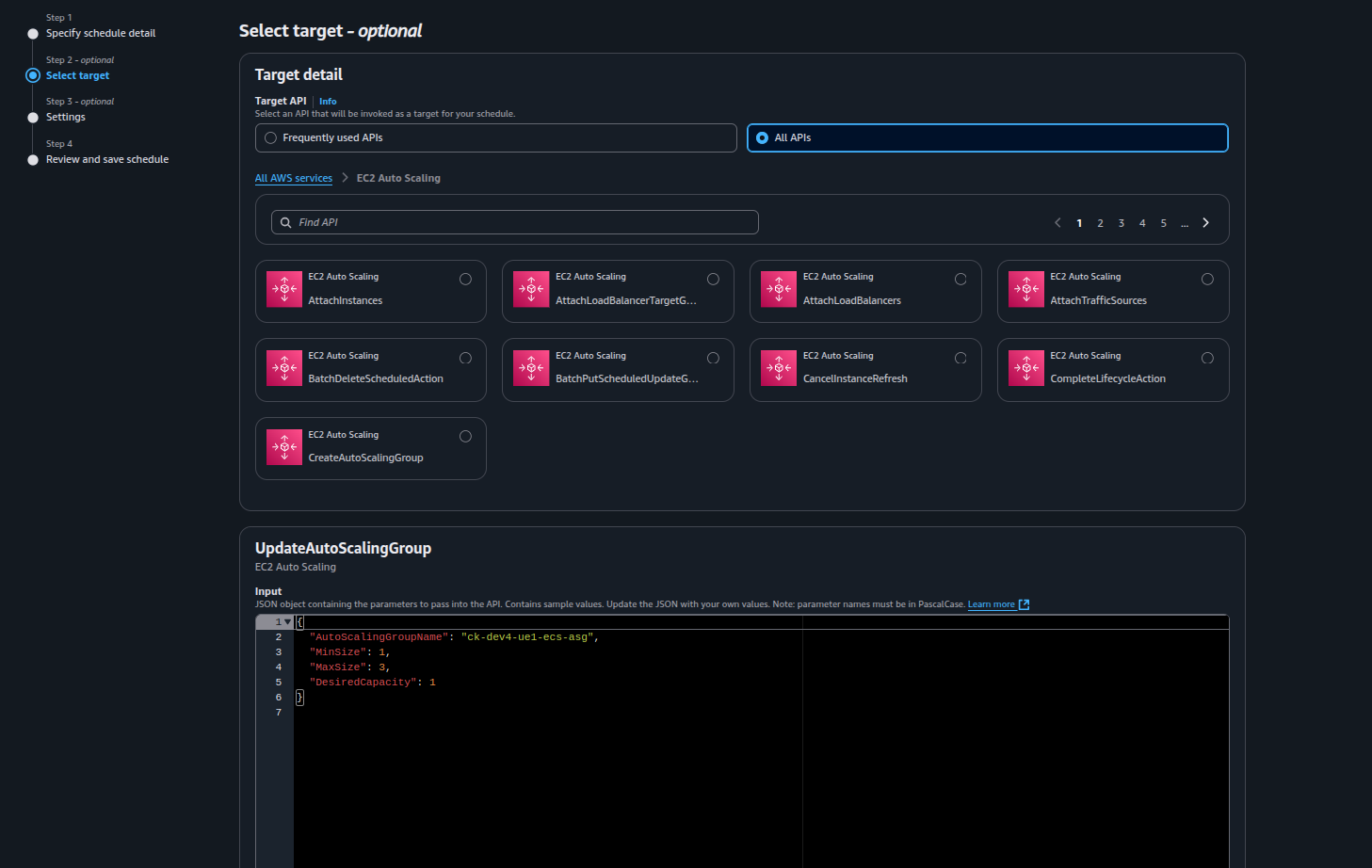
Step 2: Select Target
● Select the target type as AWS SDK operation
● Choose:
Service: EC2 Auto Scaling
Action: UpdateAutoScalingGroup
Payload: { "AutoScalingGroupName": "ck-dev4-ue1-ecs-asg", "MinSize": 1, "MaxSize": 3, "DesiredCapacity": 1
Step 3: Setting
● Configure retry behavior (e.g., 3 retries).
● Add a Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) if needed for failure tracking.
● Create a Role that has access to Update AutoScaling Group.
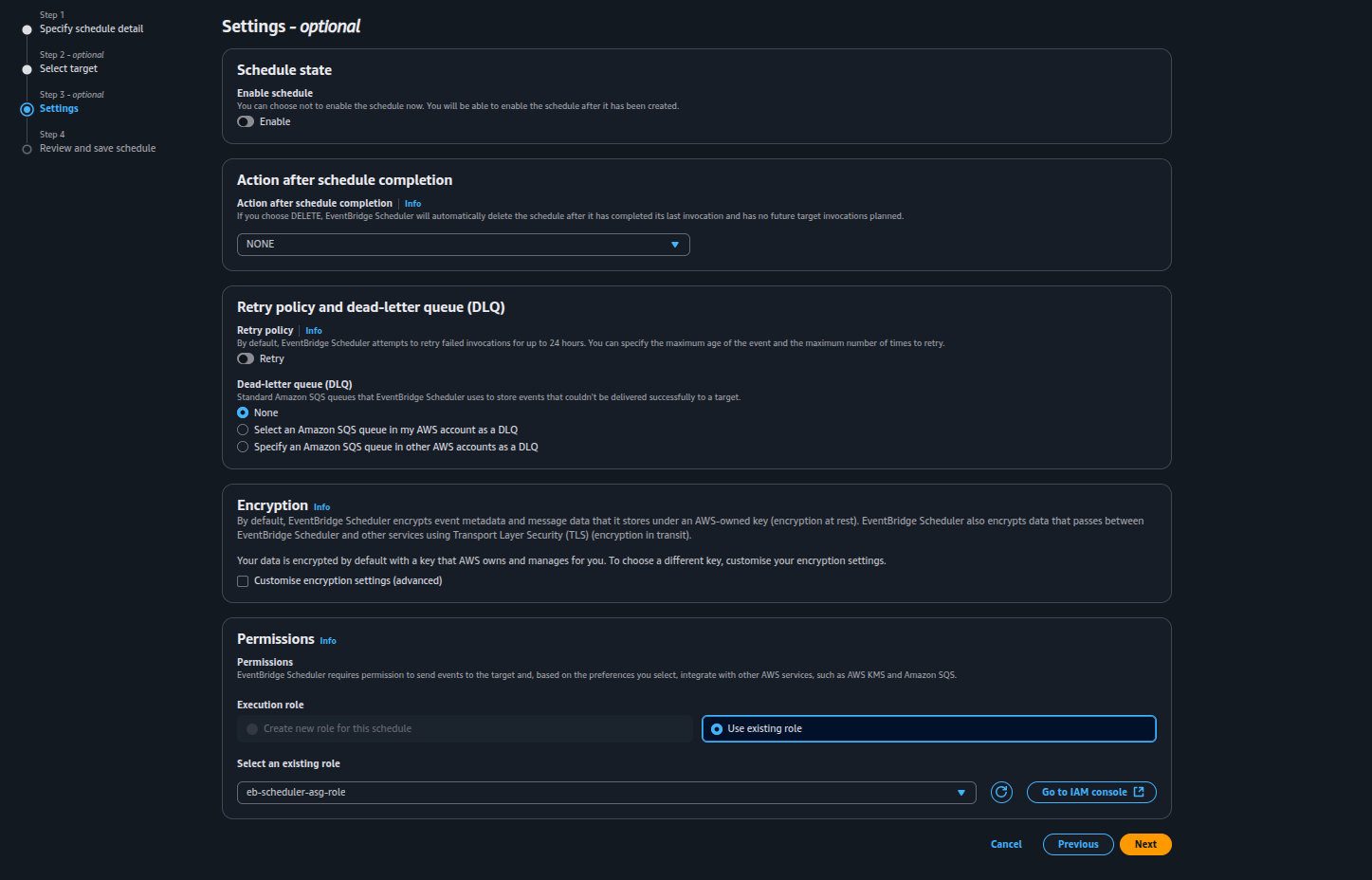
Here, we are using "*" for the resource so that the role can be used to start and stop any Auto Scaling Group. Whenever you want to perform start or stop actions on an ASG, you can use this role to set up the schedule.
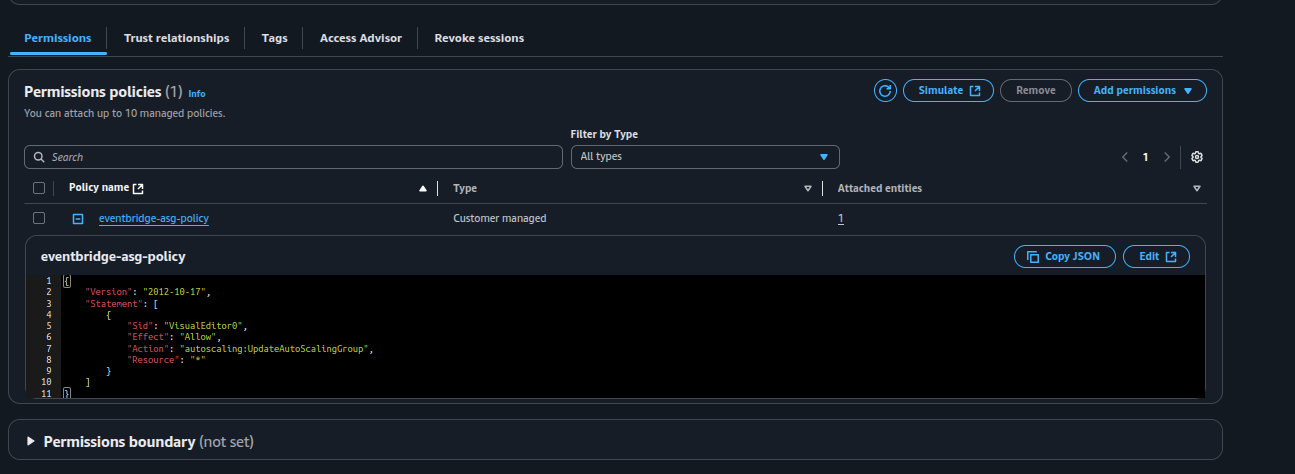
Step 4: Review and create
● Confirm details and click Create schedule.
Schedule created. It will now start your ASG every weekday at 9 AM with Give Configuration ( Maxsize, DesiredCapacity, Minsize)
Note: If you want to stop Same ASG at a specified time, same as stop operation, you need to create a new schedule for the Stop operation. With the below payload
Payload: { "AutoScalingGroupName": "ck-dev4-ue1-ecs-asg", "MinSize": 0, "MaxSize": 0, "DesiredCapacity": 0 }
This has a disadvantage for some APIs that do not support operations on bulk resources—such as ASG and ECS tasks. You need to create a separate scheduler for each ASG with its own configuration, which adds more steps and overhead when setting up resource scheduling.
Here comes CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler with a simplified approach
CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler takes a simplified, user-friendly approach to resource scheduling, eliminating unnecessary complexity and ensuring full transparency in operations. It’s an excellent choice for teams aiming to automate cloud management, cut costs, and retain control—all without dealing with complicated setup processes. Thanks to its smart design, built-in state awareness, and robust retry capabilities, Tuner Scheduler guarantees that your cloud resources are managed efficiently and reliably.
Whether you’re overseeing a handful or hundreds of instances, Tuner Scheduler transforms automation into a seamless, “set it and forget it” process. This allows you to concentrate on driving innovation, while your cloud resources are automatically managed in the background.
Getting Started is Easy
Scheduling your cloud resources with CloudKeeper Tuner takes just a few steps:
Here’s how you can get started in a few easy steps:
1. Log in: Log into your CloudKeeper Tuner dashboard.
2. Give Scheduler Access: Give Start and Stop Access to Scheduler
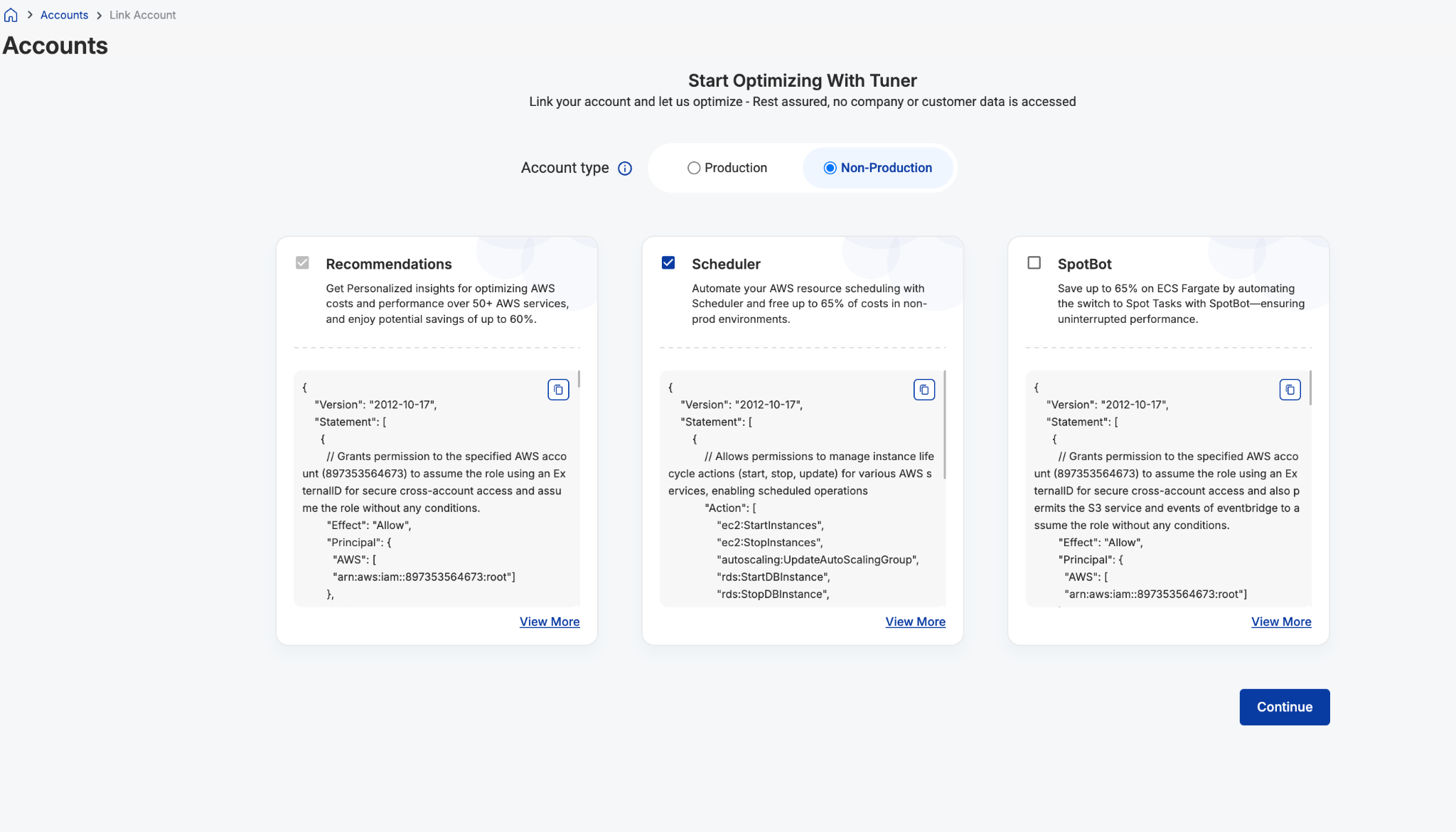
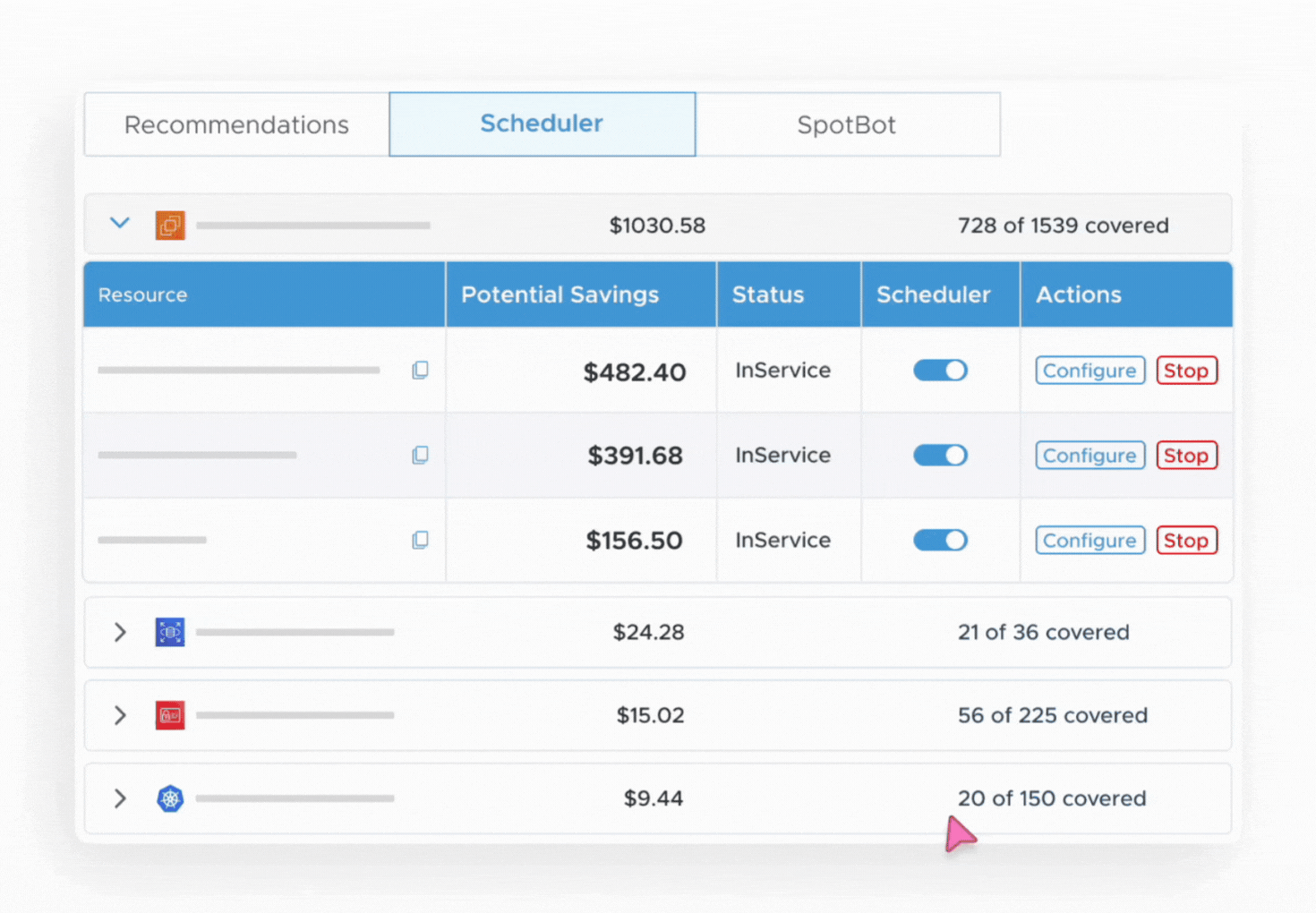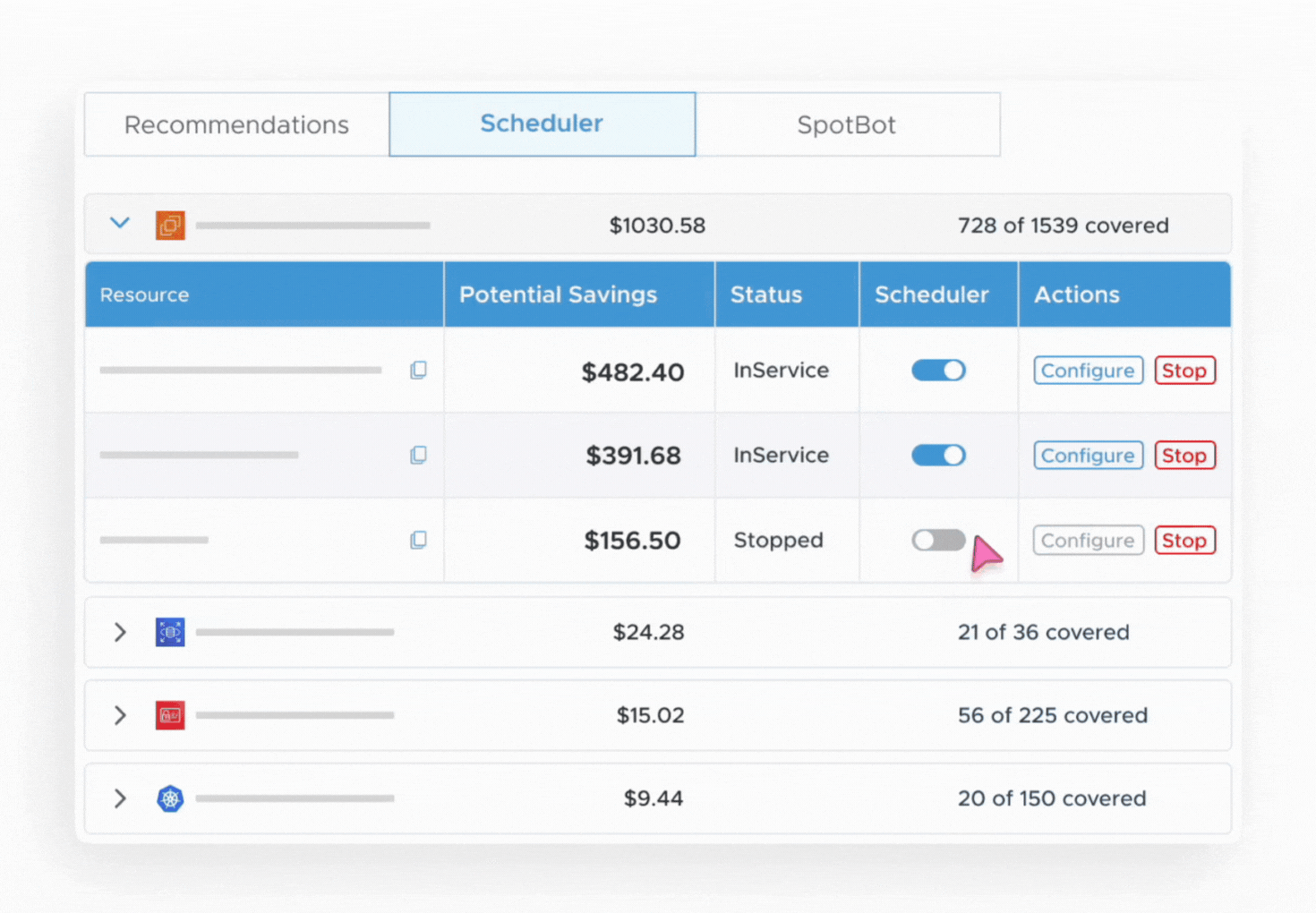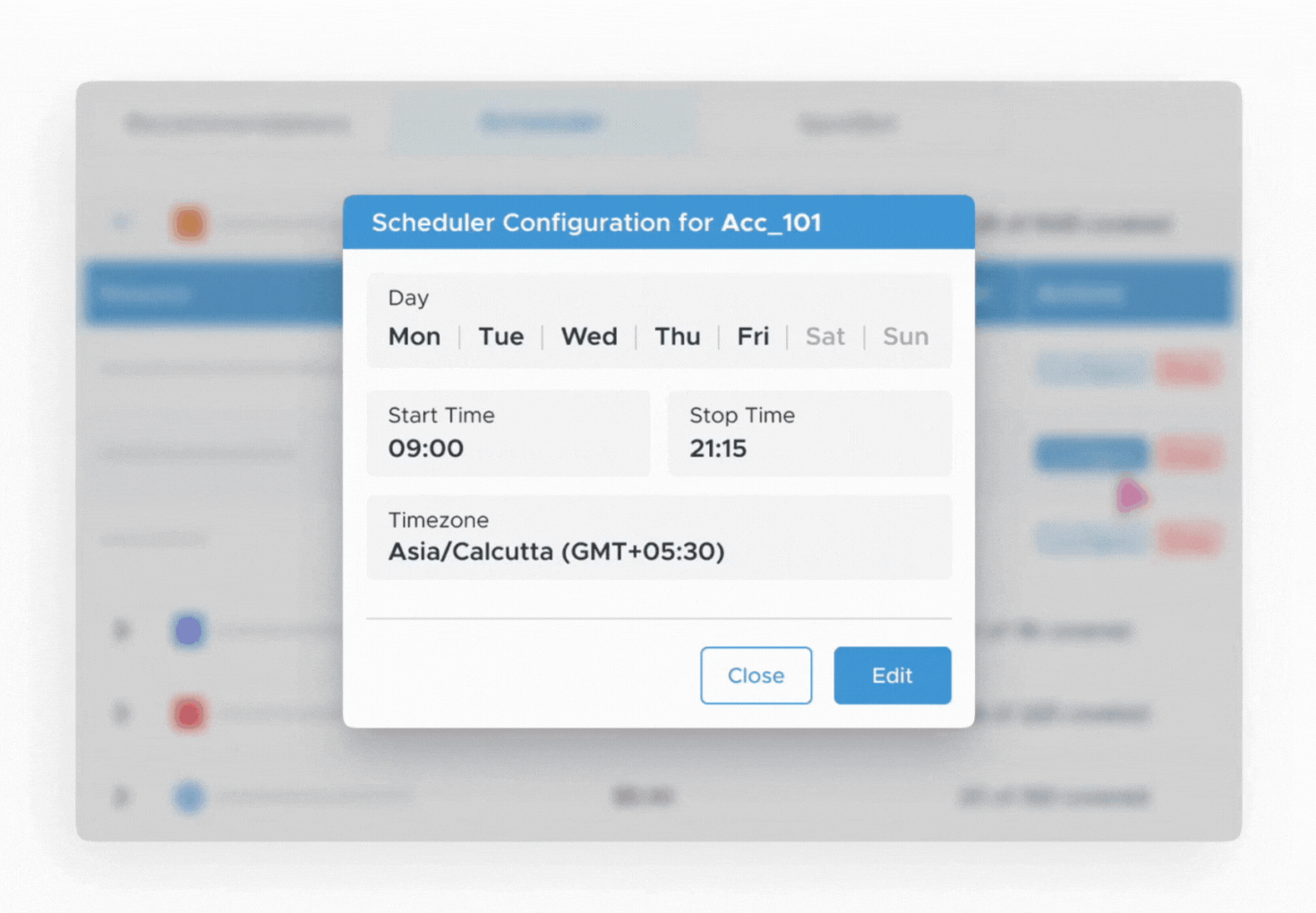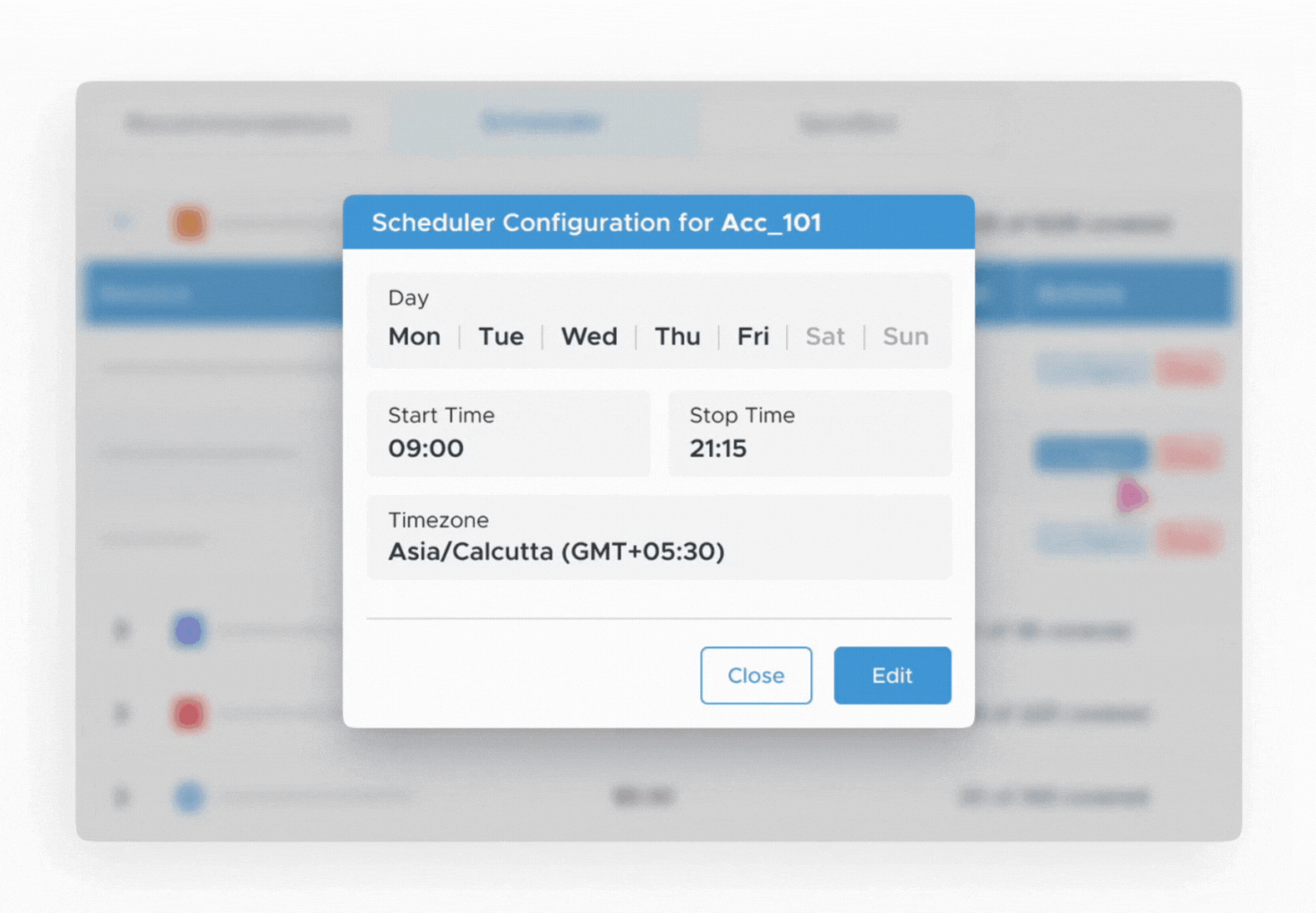
3. Enable Scheduler:
- Enable Scheduler for the Account and add the default configuration (start/ Stop time and days).This will be inherited by all the resources in the account eligible for scheduling.
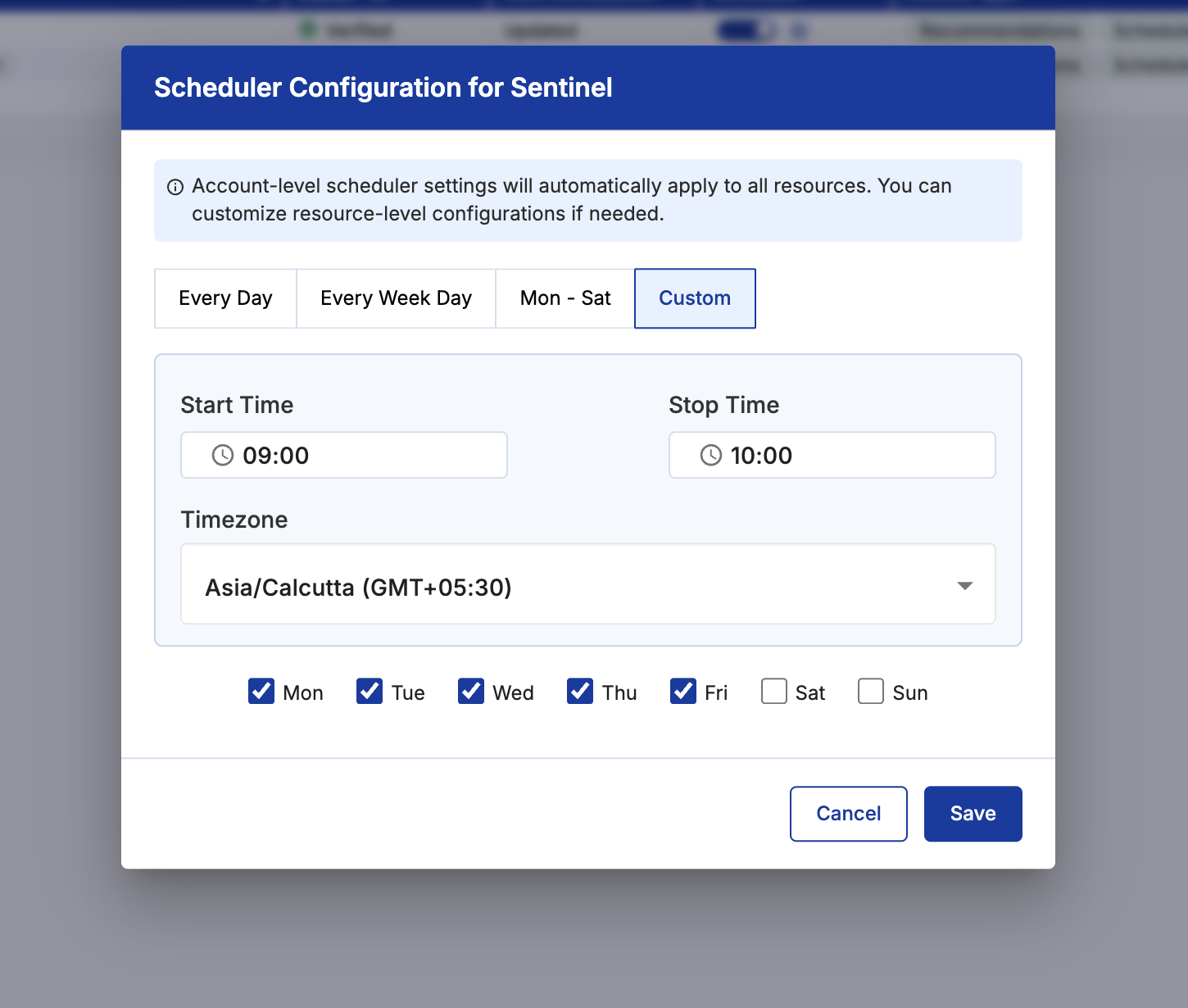
- Head to the scheduler tab and choose the resource type (EC2, RDS, etc.) you want to auto start & stop.
- Enable the scheduler for the resource, and you can set the time for start and/or stop operations at the resource level as well.
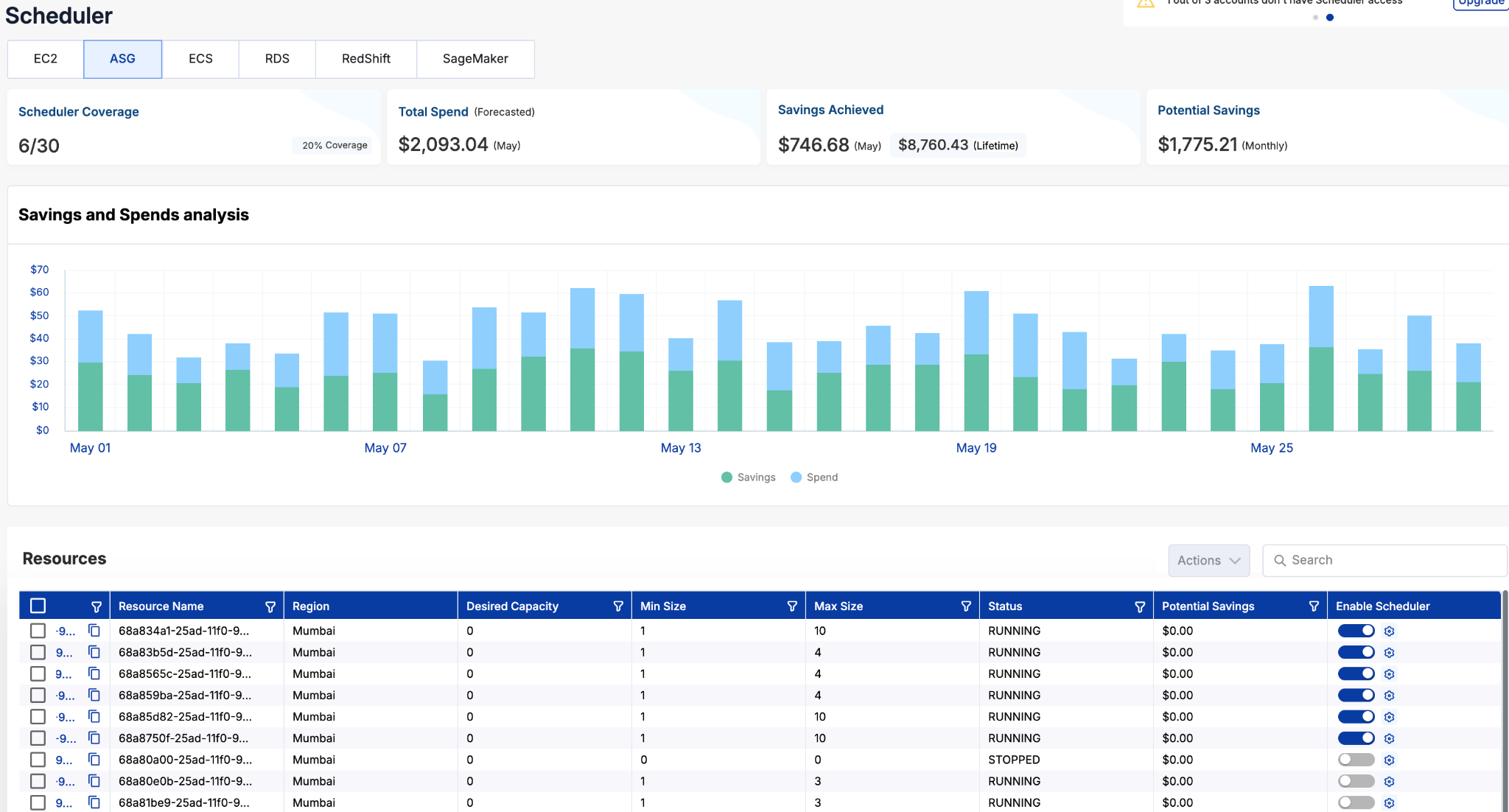
4. Auto Schedule Your Resources: Tuner will immediately begin monitoring and executing start and stop actions based on your schedule.
5. Monitor Savings: Use the dashboard to track the overall scheduling and savings achieved.
Scheduling Made Easy with Tuner
1. Easy and Simple Setup - Schedule start/stop actions quickly using a single template—no complex scripts or multiple workflows.
2. Auto Resource Detection - Tuner automatically identifies resources, so you don’t need to enter instance IDs or ARNs manually. This feature is especially valuable for managing large inventories or dynamic environments.
3. Smart Retry Handling - If an operation fails, Tuner retries the action intelligently. Once the default retry limit is reached, the scheduler waits for the next scheduled cycle, avoiding unnecessary system load.
4. Remembers Resource State - Tuner keeps track of resource states to avoid unnecessary actions, even if changes happen manually. This is especially useful in environments where manual overrides may occur, as the system ensures predictable behavior without duplicating actions.
5. Optimized for Start/Stop - Perfect for automating non-production shutdowns, helping you with cloud cost savings easily.
Conclusion
● CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler is purpose-built for AWS cost optimization, offering a streamlined, user-friendly experience for start/stop scheduling of key resources, automatic resource discovery, and state management. It is ideal for organizations seeking quick wins in cost control with minimal setup.
● AWS EventBridge Scheduler is a powerful, general-purpose scheduling engine with advanced features like flexible time windows, DLQ integration, and broad API support. It is best suited for complex automation scenarios, event-driven architectures, and environments requiring fine-grained scheduling control and grouping.
● Choose CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler for simplicity and cloud cost optimization
● Choose AWS EventBridge Scheduler for advanced, large-scale automation and orchestration.
Ready to automate your cloud savings? Try scheduling with CloudKeeper Tuner Scheduler today.

You broke down the differences well: for simple startstop in non-production environments, the template and auto-discovery in tuner make more sense, but for complex orchestrations, eventbridge wins with DLQ and flexible window. In practice, the most annoying thing is that in eventbridge, for ASG you have to keep separate schedules for start and stop and manually remember the capacity parameters. In our logs, along with scheduler events, we kept seeing weird external requests to https://crazytimeonline.org/ and had to dig in extra to figure out what actually related to infrastructure tasks. Had a similar story with http://megawheelgame.com/ and https://sweetbonanzalive.org/ when noise in the events made it hard to tell where the retries were due to throttling and where it was just junk. So I get the idea about built-in "state memory" in tuner, but DLQ in eventbridge still sometimes saves the day when debugging failures.
Great comparison between CloudKeeper Tuner and AWS EventBridge Scheduler! What I like most is how CloudKeeper simplifies automation — it reminds me a bit of https://snake-game.io