Senior Software Engineer
Varshit is a Senior Software Engineer with over five years of experience in DevOps and Platform Engineering.
In today's cloud-native landscape, API gateways play a critical role in serverless and microservices architectures. This is a powerful tool for building scalable APIs, but it's also easy to overlook the cost-effectiveness, especially if the APIs are frequently called or redundant. For FinOps practitioners who are sure to focus on reducing costs without compromising, the use of API Gateways integrated with a cache is a game-changer.
Amazon API Gateway provides integrated response caching, interfering with edge layer endpoints, eliminating the need to access back-end services (such as Lambda, EC2, RDS) for each request.
Here’s how it works:
1. Reduce Backend Invocation Costs
Back-end views (such as Lambda or RDS calls) often incur the majority of API-related costs. These calls are avoided in intermediate storage if the same query from the cache is being operated on.
2. Control Data Transfer Charges
Output data transmission (especially for large payloads) is reduced, leading to savings in data transmission costs (DTO).
3. Enhance User Experience
Faster response times and lower latency mean you don’t need to scale up infra (saving both cost and operational effort).
Suppose you want to run the Product Catalog API for your e-commerce platform. To retrieve the product listings.
Without caching:
With Caching Enabled:
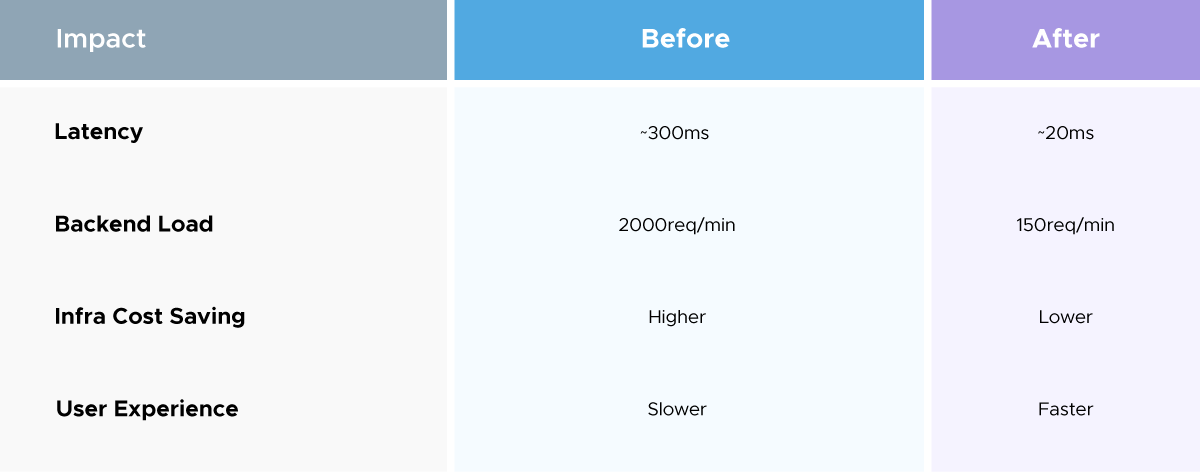
Multiplying this by multiple APIs can save thousands of dollars each year.
Sign in to the API Gateway console.
Note: If you have an existing setting for a method-level cache, changing the default method-level caching setting doesn't affect that existing setting.
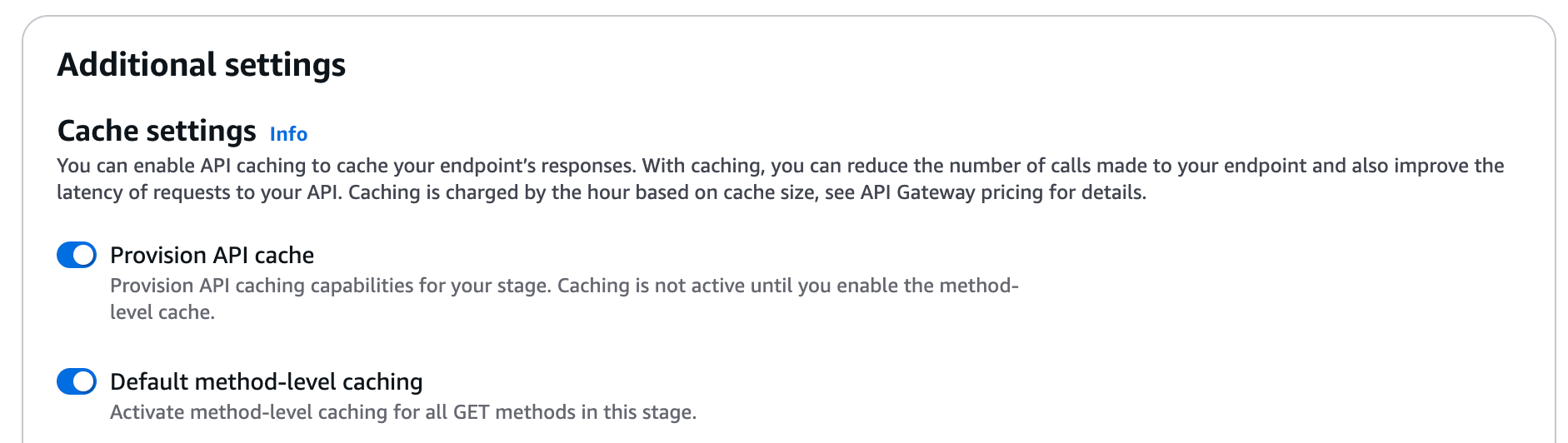
Choose Save changes.
For more information, please refer to the Amazon official Document.
Pro Tip:
Use stage variables to toggle caching across environments without redeploying code.
Ideal For:
Avoid Caching When:
Data changes frequently (e.g., real-time stock prices).
You require request-by-request freshness (e.g., personalized responses).
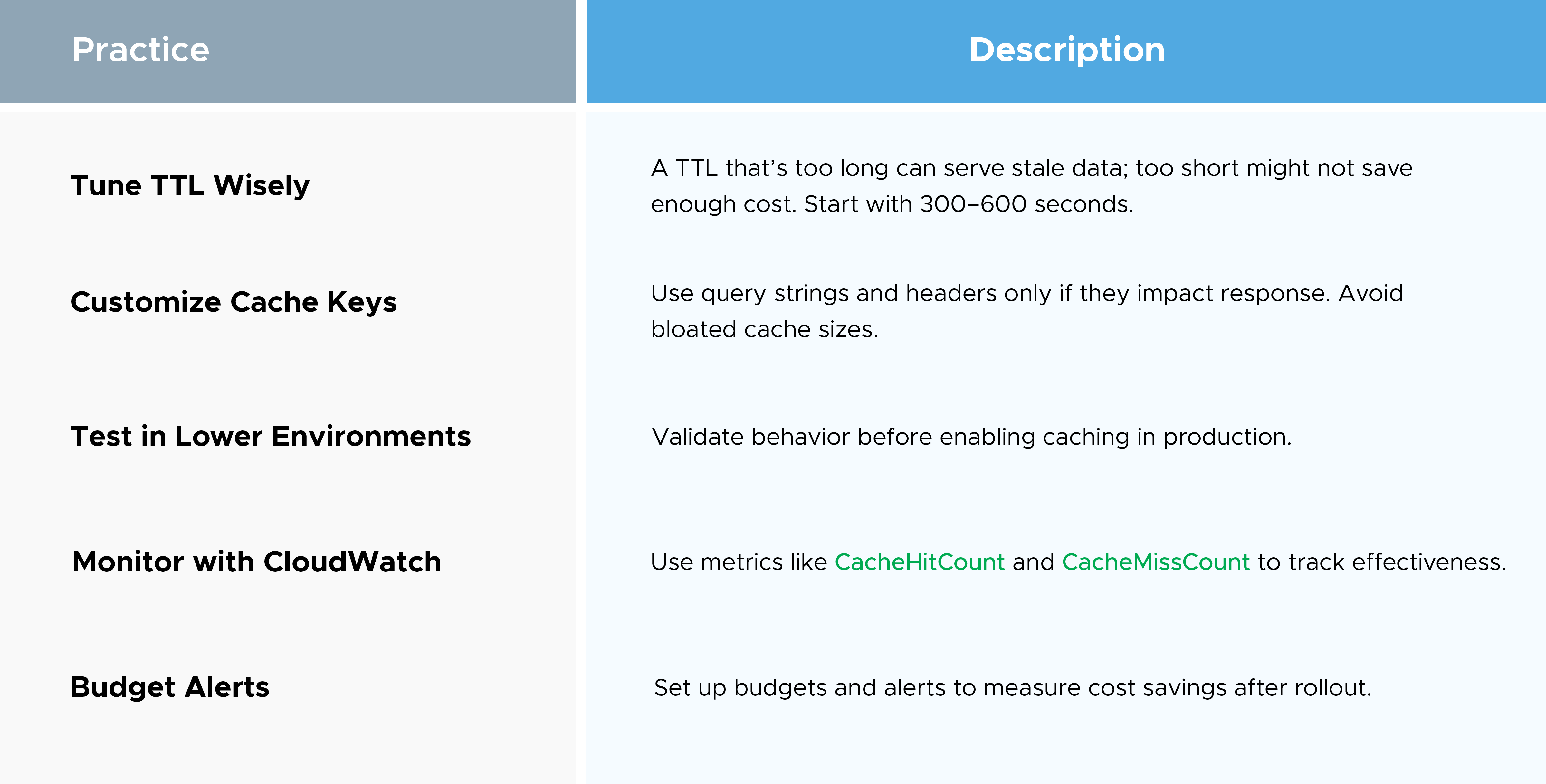
API Gateway Caching is one of the easiest ways to reduce costs and improve performance. Doing more in less amounts. If you're managing serverless APIs or want to advise your team on cost strategies, put caching in your roadmap today.
Speak with our advisors to learn how you can take control of your Cloud Cost