DevOps Engineer
Jatin is an AWS-certified SysOps Administrator Associate with extensive expertise in AWS cloud services and a broad spectrum of DevOps tools.
In today’s always-on world, reducing downtime is crucial. Disaster recovery (DR) strategies enable businesses to quickly recover from outages and maintain service availability. Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable Domain Name System (DNS) service that plays a key role in DR by routing traffic between on-premises infrastructure and AWS Cloud resources.
This blog looks at how to use Route 53 failover routing policies to create resilient disaster recovery architectures that connect both on-premises data centers and AWS.
Disaster recovery involves restoring operations after unexpected failures caused by hardware problems, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. AWS offers several DR strategies, ranging from simple backups to multi-site active/active deployments.
Amazon Route 53 provides resilience by giving DNS-level control over traffic distribution. Its features, like health checks and failover routing, can detect outages and redirect clients to healthy endpoints, ensuring minimal downtime.
Key DR methods supported by Route 53 include:
The failover routing policy directs traffic to a primary resource under normal conditions and to a secondary resource during an outage.
How It Works
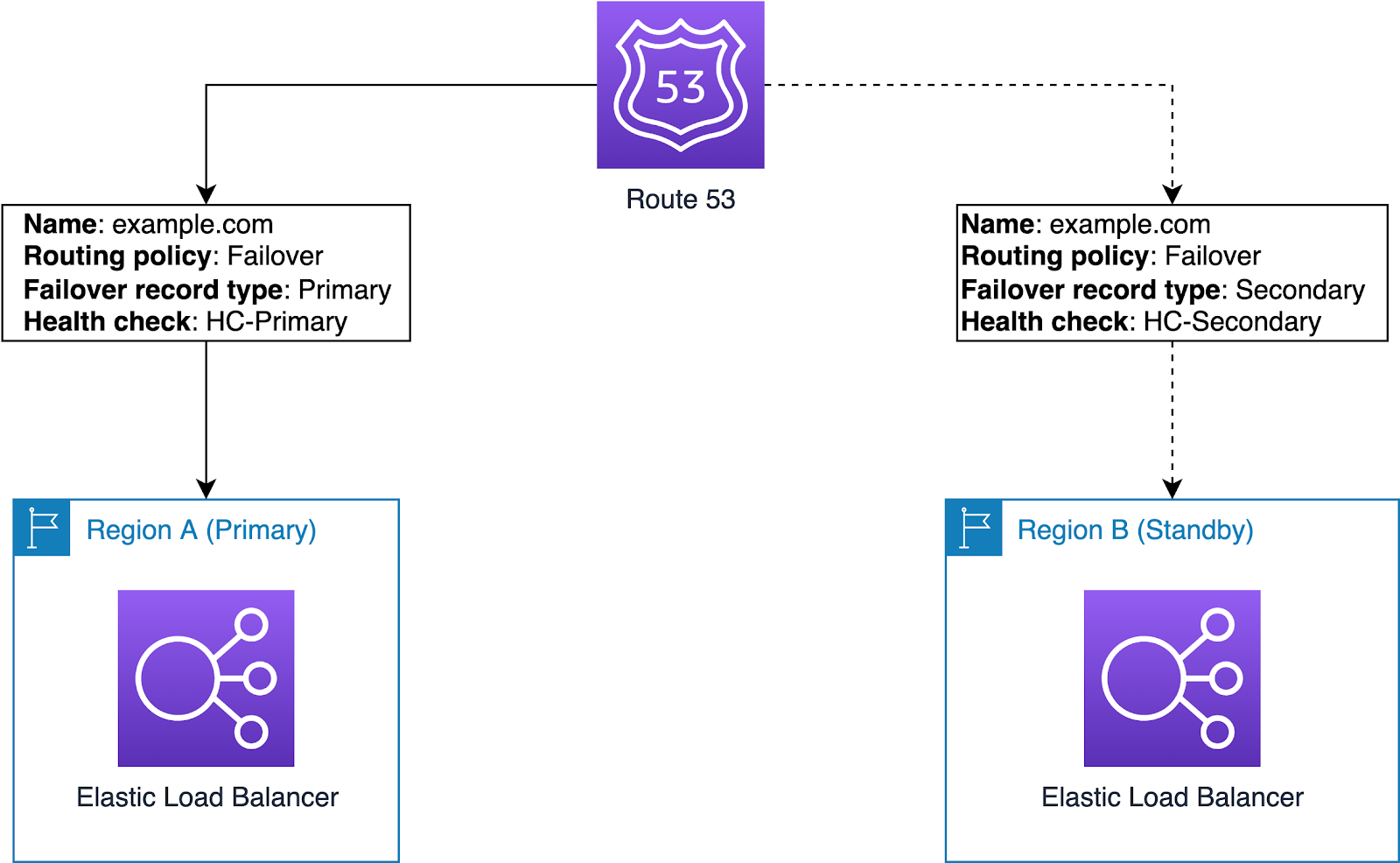
This policy helps organizations blend existing infrastructure with AWS resources, ensuring high availability. For instance, it would lead to high availability of Amazon Aurora, which is critical for maximum uptime.
A hybrid DR plan uses both on-premises and AWS resources, which lowers costs and enhances resilience.
Key Components
Steps to Implement
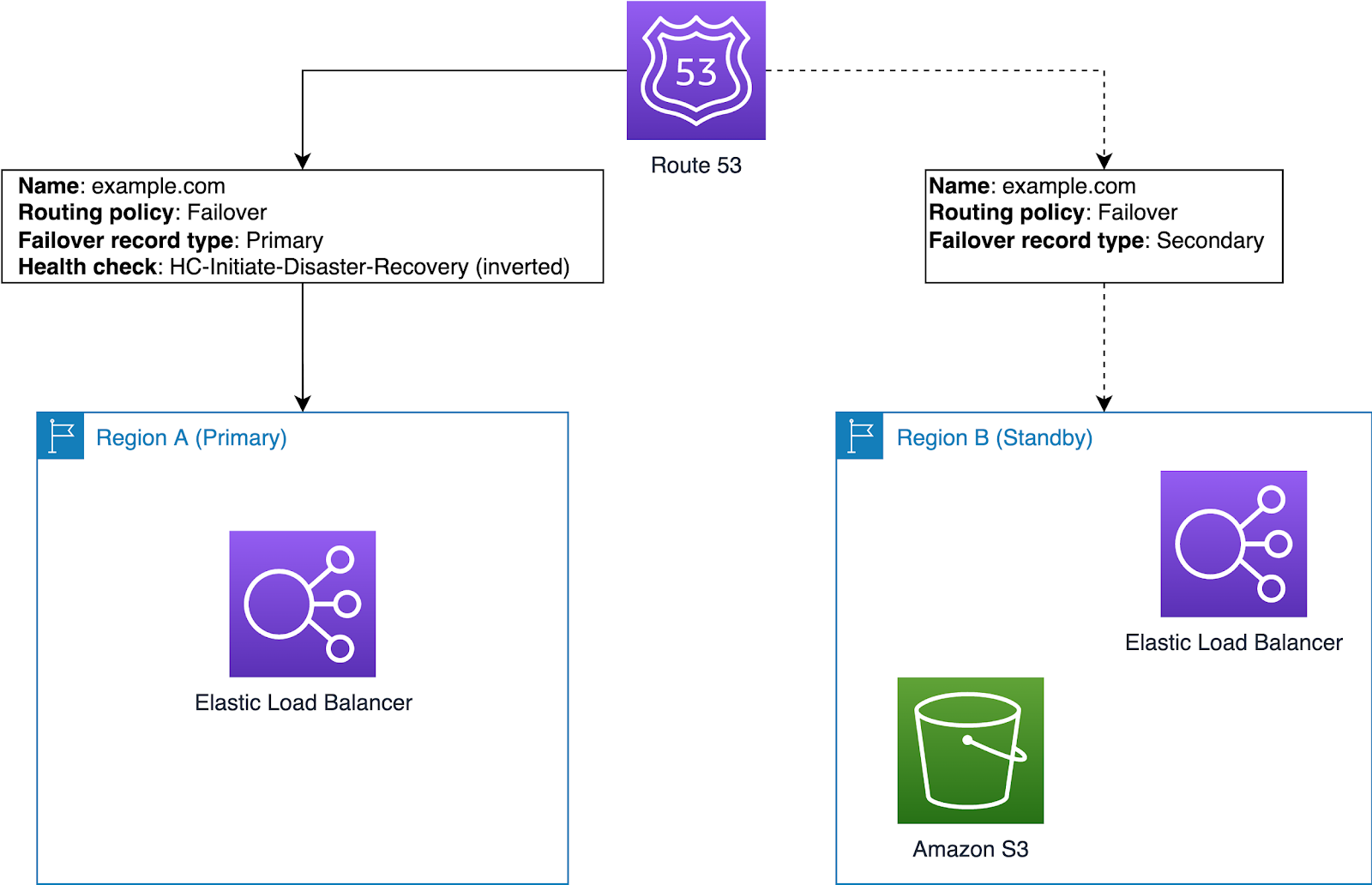
By combining Amazon Route 53 failover routing with a hybrid architecture, organizations can create a strong disaster recovery solution that protects both on-premises and cloud workloads. Whether using a pilot light, warm standby, or multi-site strategy, Route 53 supports automated, reliable failover with minimal complexity.
Investing in a solid DR plan ensures business continuity, protects against data loss, and maintains customer trust, all backed by the flexibility of AWS and Route 53.
Speak with our advisors to learn how you can take control of your Cloud Cost
https://geometrydash-lite2.io/ is a fast-paced arcade platformer that combines music, timing, and precision into an addictive experience.