DevOps Engineer
Abhay Joshi is a problem solver who enjoys playing with algorithms and building scalable distributed systems.
This guide shows how to deploy KEDA on an Amazon EKS cluster and autoscale a simple AWS SQS consumer Deployment (sqs-worker) based on the number of messages in an Amazon SQS queue. AWS authentication is handled using Amazon EKS Pod Identity (no static AWS keys in Kubernetes).
KEDA is a Kubernetes-based Event Driven Autoscaler. With KEDA, you can drive the scaling of any container in Kubernetes based on the number of events needing to be processed.
KEDA is a single-purpose and lightweight component that can be added to any Kubernetes cluster. KEDA works alongside standard Kubernetes components like the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler and can extend functionality without overwriting or duplication. With KEDA, you can explicitly map the apps you want to use event-driven scale, with other apps continuing to function. This makes KEDA a flexible and safe option to run alongside any number of other Kubernetes applications or frameworks.
KEDA creates external metrics from event sources and feeds those metrics to Kubernetes HPA.
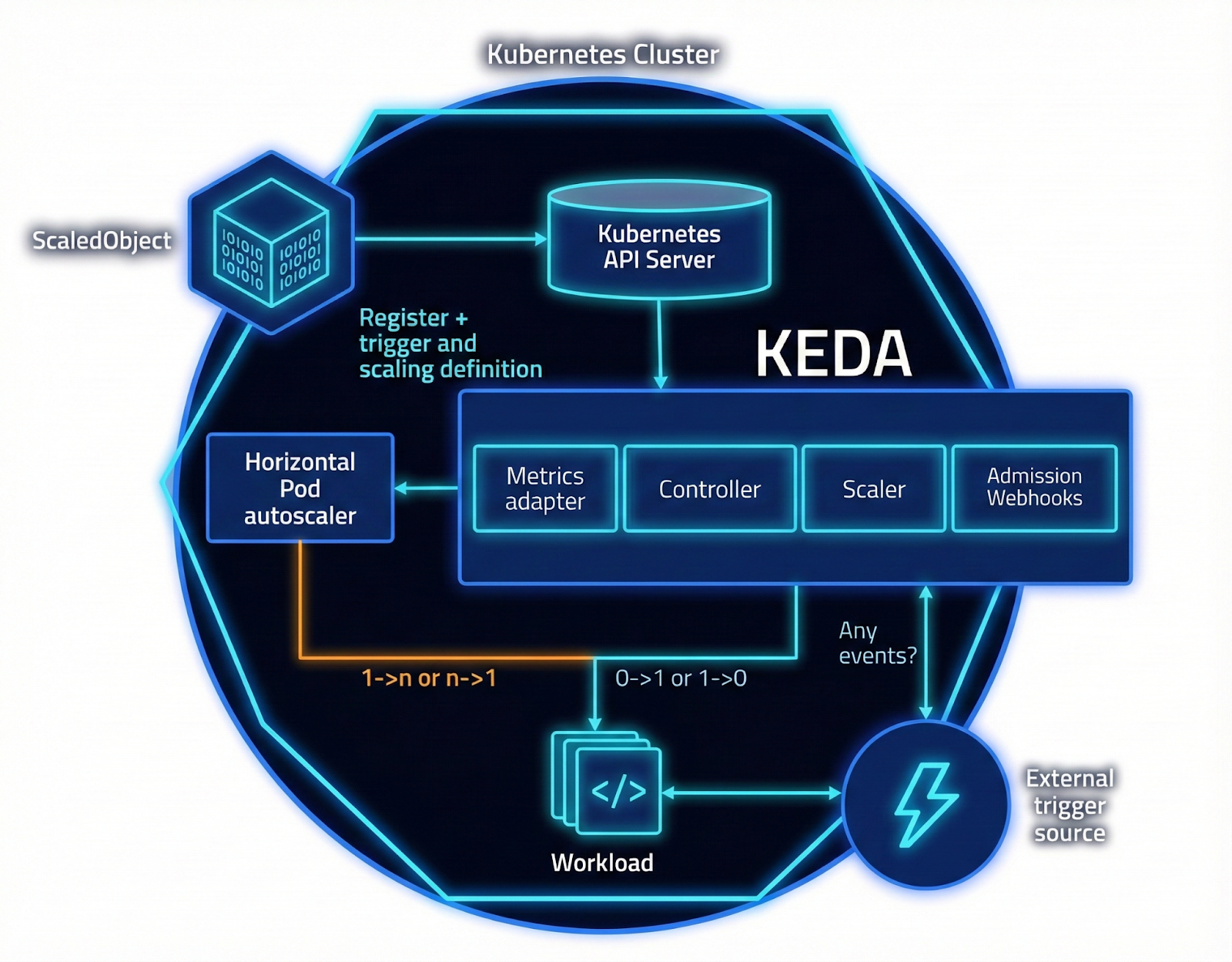
In this POC, KEDA polls an Amazon SQS queue and scales a Kubernetes Deployment. Read more about Kubernetes deployment and management.
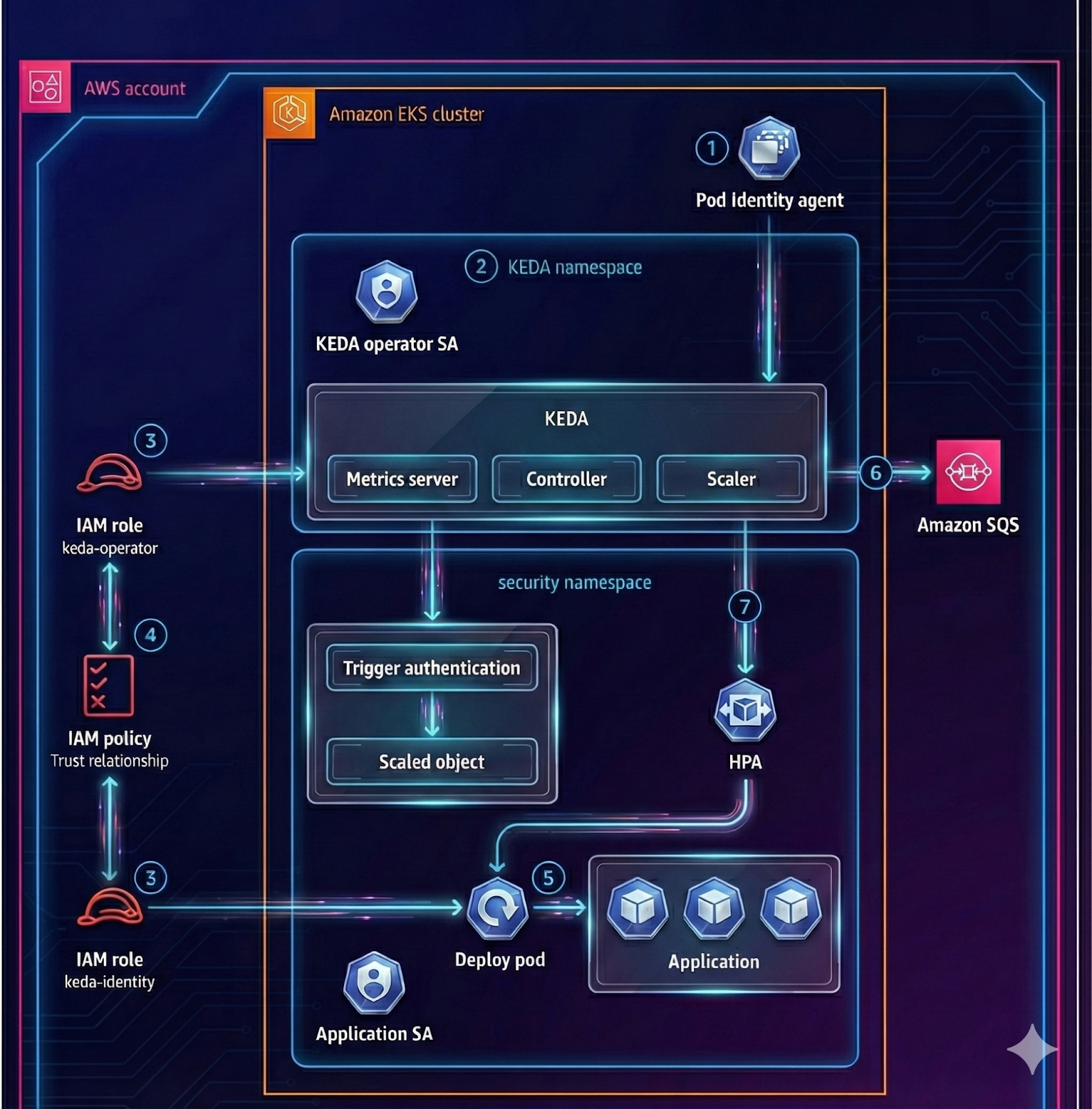
You need:
Set these variables to match your environment:

Create a standard Amazon SQS queue and capture its URL:

Install the Amazon EKS Pod Identity agent. If you are using EKS Auto Mode, the agent is built-in and you can skip this step.

Verify the agent is running on nodes:

Install KEDA into the dedicated namespace keda using Helm:
Create two IAM roles:
KEDA operator role: reads AWS SQS queue attributes for scaling.
Worker role: receives and deletes messages.
Both roles use a Pod Identity trust policy with principal pods.eks.amazonaws.com.
Attach POC-friendly permissions (tighten later to least privilege):
Create the application namespace and service account:
Associate IAM roles with Kubernetes service accounts: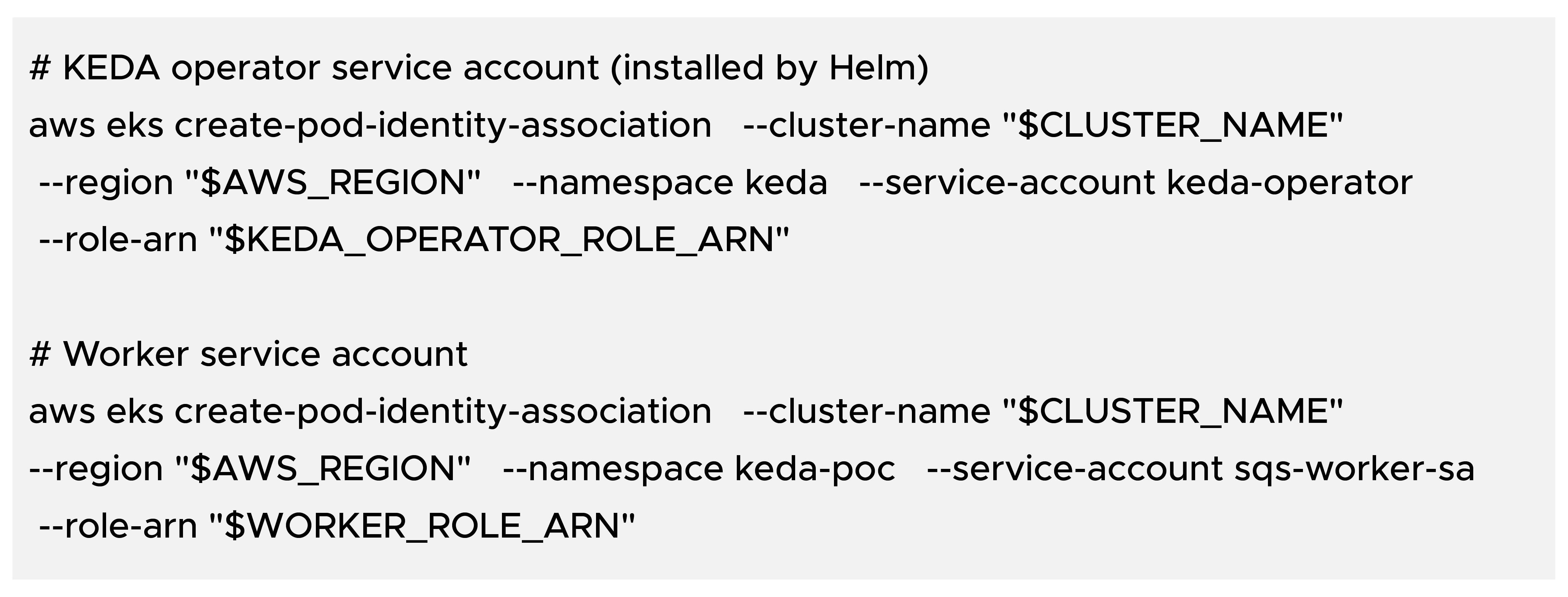
Restart the KEDA operator to pick up the new identity (recommended):

Create worker.yaml:

Replace the placeholder and apply:
Create keda-sqs.yaml: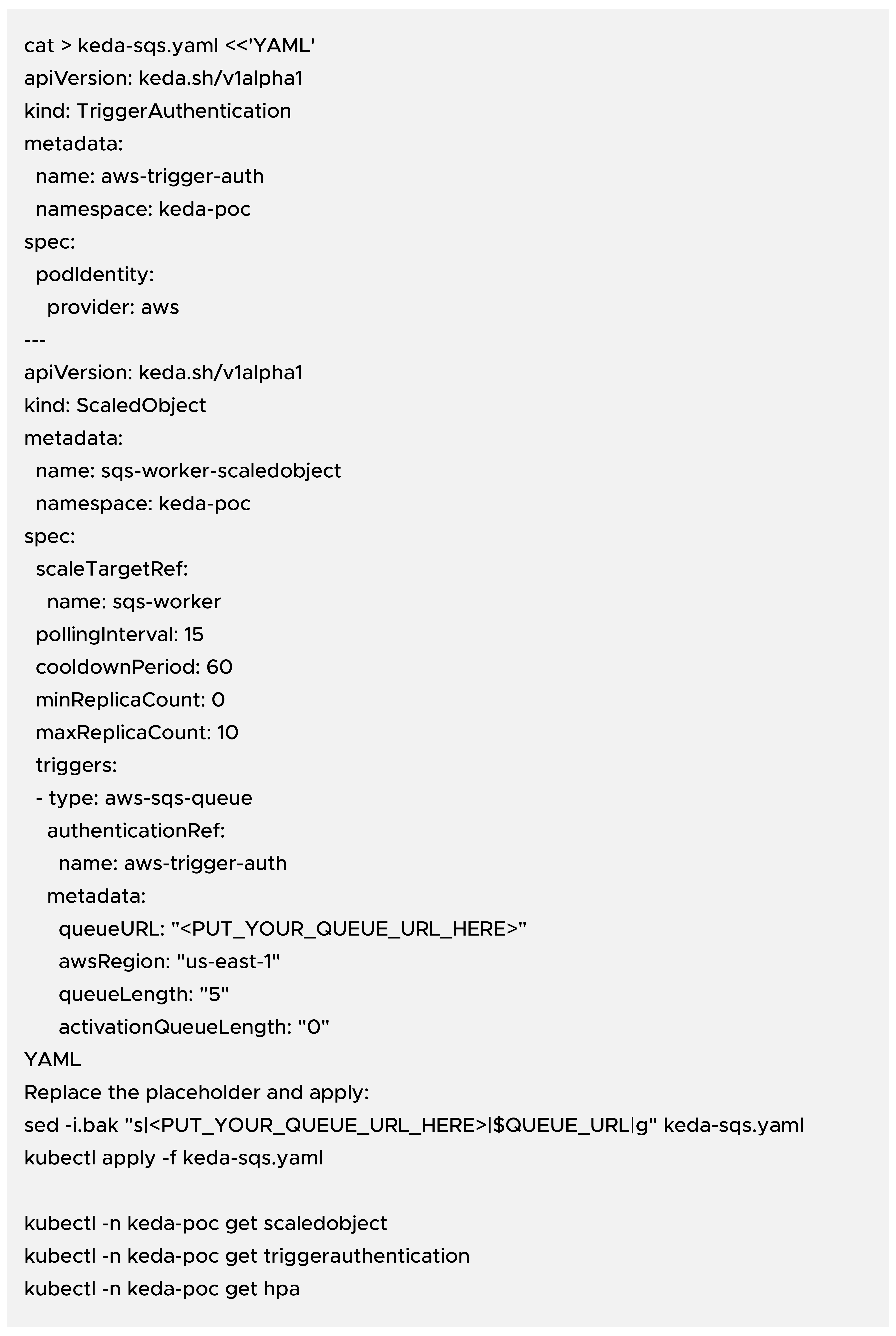
Watch the Deployment/HPA and pods:
Send messages to SQS (example: 50 messages):
Expected behavior: when the queue has unread messages, KEDA activates the HPA and scales the Deployment up. After the worker drains the queue and cooldownPeriod passes, it scales back down to 0.
Useful commands during the POC:
Remove Kubernetes resources:
Optionally uninstall KEDA:
Remove IAM roles (example):

Speak with our advisors to learn how you can take control of your Cloud Cost